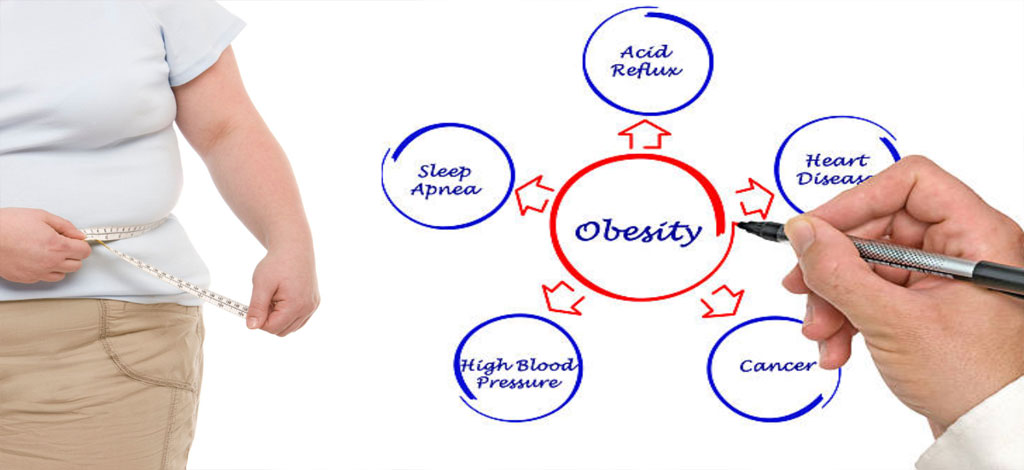
Obesity
Obesity is a medical condition characterized by the excessive accumulation of body fat, to the point where it may have a negative impact on health. It is often determined by the body mass index (BMI), which is a ratio of weight to height. A BMI of 30 or higher is generally classified as obese.
- Dietary Habits: Consuming high-calorie, low-nutrient foods, especially those high in sugars and fats, can contribute to weight gain.
- Genetics: Genetic factors can influence an individual's predisposition to obesity by affecting metabolism and fat storage.
- Environmental Factors: Factors such as a lack of access to healthy food options, built environments that discourage physical activity, and cultural influences can contribute to obesity.
- Psychological Factors: Emotional factors, stress, and certain mental health conditions may contribute to overeating and weight gain.
- Medical Conditions: Some medical conditions, such as hypothyroidism or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS), can contribute to weight gain.
Causes of Obesity:
- Cardiovascular Issues: Obesity is a major risk factor for heart disease and can contribute to conditions like hypertension and high cholesterol.
- Type 2 Diabetes: Obesity is a significant risk factor for the development of Type 2 diabetes.
- Joint Problems: Excess weight puts strain on the joints, leading to conditions like osteoarthritis.
- Respiratory Issues: Obesity can contribute to respiratory problems, including sleep apnea and asthma.
- Liver Disease: Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is more common in individuals who are obese.
- Psychological Impact: Obesity can contribute to low self-esteem, depression, and other mental health issues.